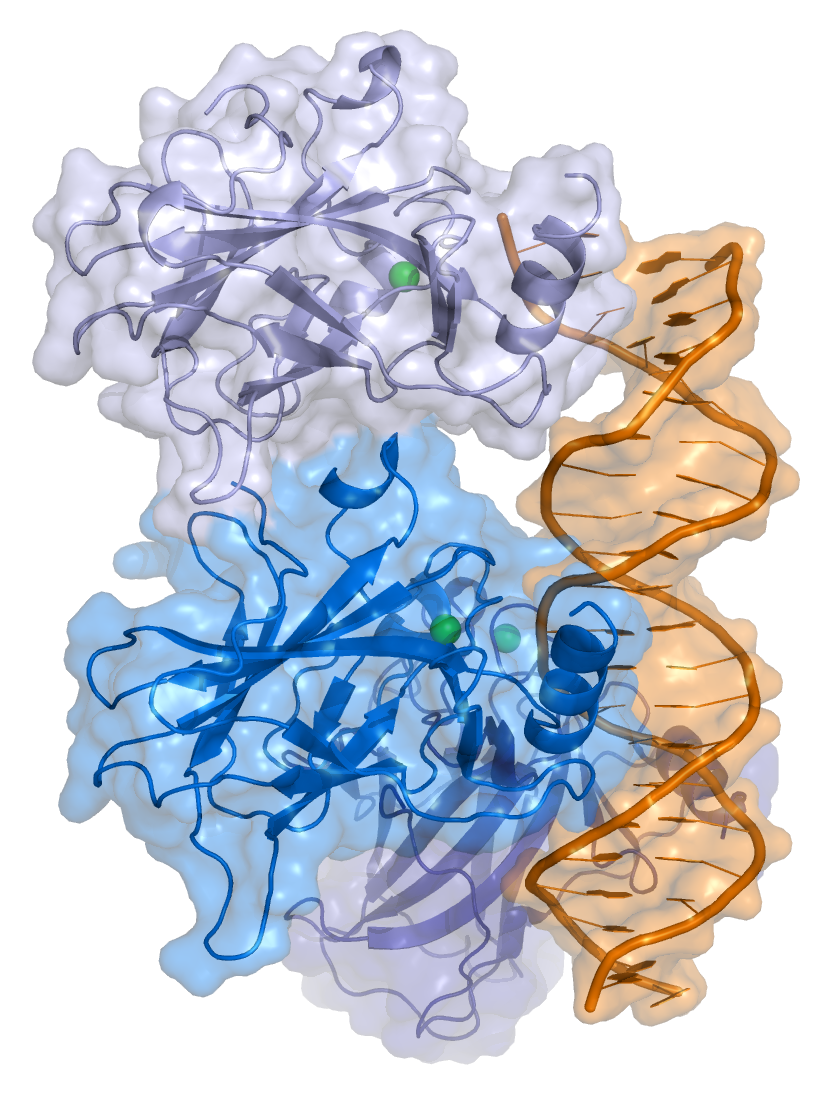
p53 is an incredible protein whose function is to stop the neoplastic transformation and tumor progression. It acts like a collector of stress inputs and coordinator of pathways that protect cellular homeostasis and genome stability.
The missense mutations in the TP53 gene are very dangerous because a mutant p53 protein lose its tumor suppressive activities. In this scenario cancer cells acquire advantages thanks to the mutant p53 and its pathway promote the invasion, metastasis and chemoresistance.
It could be understood how p53 it’s important in the tumor growth in fact the alternated form of this protein,TP53, is the most frequently altered gene in human tumors.
The first outcome of TP53 mutations is the loss of some p53 functions, the cell loses its suppressive responses, like senescence and apoptosis.
These selective advantages come from retaining only the mutant form of the p53 protein, so the wild-type p53 is lost.
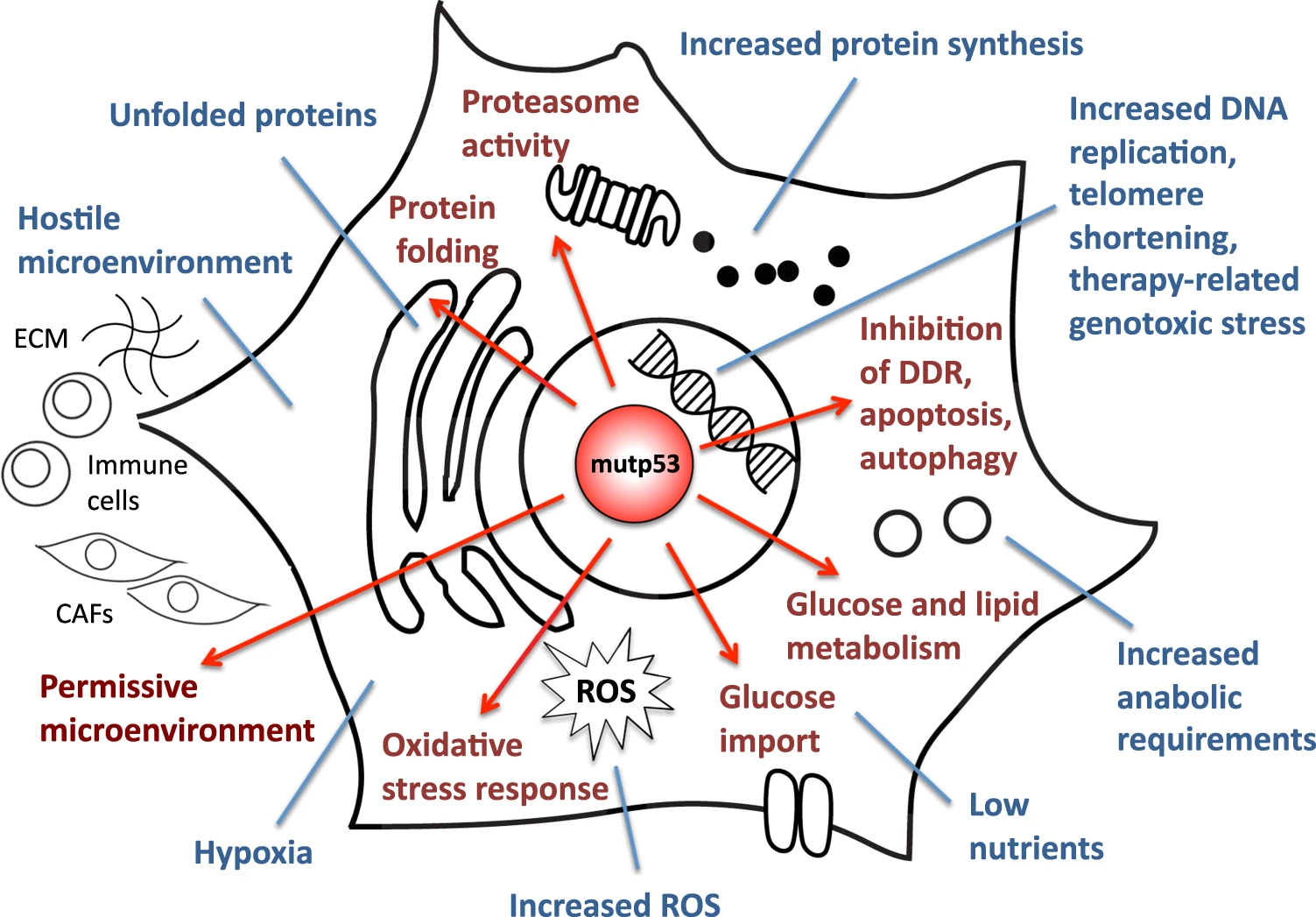
In this image the blue lines represent the stress inputs, the red ones are the adaptive mechanisms.
The mutp53 helps the survival response to oxidative stress, increase the proteosome activity in human cancer cell, inhibit the DDR, DNA-damage response in HUPKI (Humanize mutp53 knock-in mice), promote the angiogenesis in breast cancer.
The post-translational modifications are triggered by cancer-related stress stimuli.
When the mutp53 is accumulated the mechanism of autophagy-mediated degradation is suspended by the acetylation of C-terminal lysine; the modifications also enhance mutp53 oncogenic activities that promote breast cancer cells proliferation and chemoresistance.
Another post-translational modification enhances the ability of mutp53 to neutralize p63 anti-metastatic activity.
The Warburg effect consist in adaptation of cancer cells by increased glucose uptake by aerobic glycolysis. This mechanism feeds tumor growth in hypoxic conditions and due to extracellular acidification the immune system surveillance is held back.
- Cancer cell survival under stress conditions by the inhibition of the apoptotic and autophagic mechanism.
- Chemoresistance by the repression of p73 pro-apoptotic transcriptional program.
- Suppression autophagy in tumor cell, in fact inhibits AMPK kinase that under metabolic stress stimulates autophagy.
- Inhibition of the anti-metastatic p63 target gene Sharp1.