“We are what we eat“ it is a well-known statement by german philosopher Ludwig Fuerbach.
Nutrition sometimes has not much importance unless one is on a path aimed at losing weight.
However a balanced diet plays a key role in health.
A balanced caloric intake in addition to making you longer-lived and protects against a number of diseases, such as cancer. In contrast, a caloric deficit weakens the immune system and complicates wound healing.
It might give pause to ponder the European obese rate of 59% in adults while one of three children are overweight or suffer from obesity.
The obesity is defined as when body weight is greater than the correct body weight/height ratio.
One way to detect obesity is by measuring body mass index (BMI). In adults, a BMI value between 25.0-29.9 is a sign of overweight, while if above 30.0 it detects obesity.
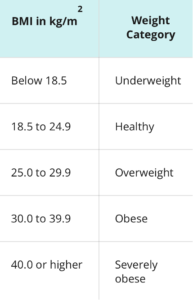
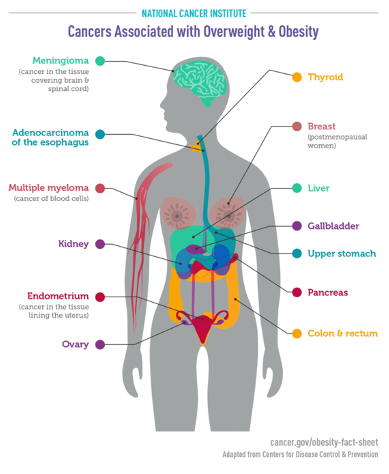
A BMI of 25.0 or higher increases the risk of developing as many as 13 types of cancer. However, this does not mean that you will definitely have cancer development.
Studies published in the “Cancer journal for clinicians” and “Nature” show that being overweight is responsible for 4% of cancers diagnosed each year worldwide.
38 genes were identified as perfectly overlapping between obese individuals and cancer patients.
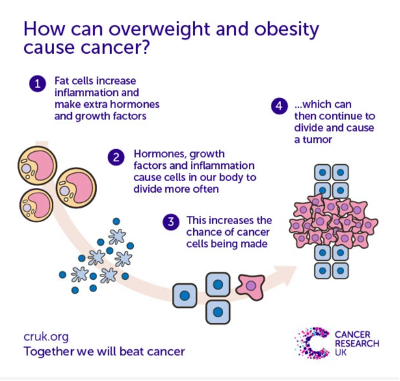
How obesity increases cancer risk:
- adipose tissue produces excessive amounts of estrogen; high levels of estrogen are associated with increased uncontrolled proliferation;
- high blood levels of insulin and igf1, hyperinsulinemia;
- obese and overweight people have chronic inflammatory conditions leading to oxidative stress leading to DNA damage;
- adipose cells produce leptin; high levels of leptin promote aberrant cell proliferation;
- microbes living in the gastrointestinal tract, the gut microbiota, in obese people there is dysbiosis, which is an imbalance in the community of these gut microbes. This imbalance is associated with inflammation and altered metabolism that may be linkable to cancer development;
- overweight and obesity disorient our immune system, macrophages are drawn into tumor tissue and “reprogrammed,” such macrophages are referred to as Tumor Associated Macrophages (TAMs), resulting in being disarmed of their anti-tumor functions and diverted to contribute to the growth and spread of diseased cells. The tumor thus gains a double advantage: it reduces our defenses and corrupts them in its favor.
Reducing the risk of obesity is not a difficult feat, all you need to do is eat a healthy diet in line with your body and exercise at least thirty minutes every day. The latter if regular not only prevents obesity but also diseases such as depression.